Dallas Mavericks forward Davis has undergone surgery to repair a detached retina, team sources confirmed Friday. The injury, which forced him out of recent games, raised immediate concerns about his availability for the remainder of the season. The procedure, performed successfully, marks a critical step in his recovery process as the Mavericks assess his timeline for return. Further updates on Davis’ condition are expected in the coming days.
Mavs Forward Davis Undergoes Surgery to Repair Detached Retina
Davis underwent a successful procedure earlier this week to address the detached retina, a serious eye condition that threatened to impact his season with the Dallas Mavericks. Medical sources indicate that the forward reacted promptly to symptoms, allowing surgeons to perform the operation before any permanent vision loss occurred. Recovery is expected to take several weeks, with the team closely monitoring his progress as he begins the rehabilitation process.
- Type of Surgery: Vitrectomy with laser photocoagulation
- Estimated Recovery Time: 6-8 weeks
- Next Steps: Regular ophthalmological evaluations and gradual return to non-contact training
| Condition | Symptoms | Urgency |
|---|---|---|
| Detached Retina | Floaters, flashes, vision loss | Immediate |
| Post-Surgery Care | Eye patch, limited movement | Critical |
| Return To Play | Gradual, physician approved | Weeks to months |
Medical Experts Explain the Risks and Recovery Process for Retinal Detachment
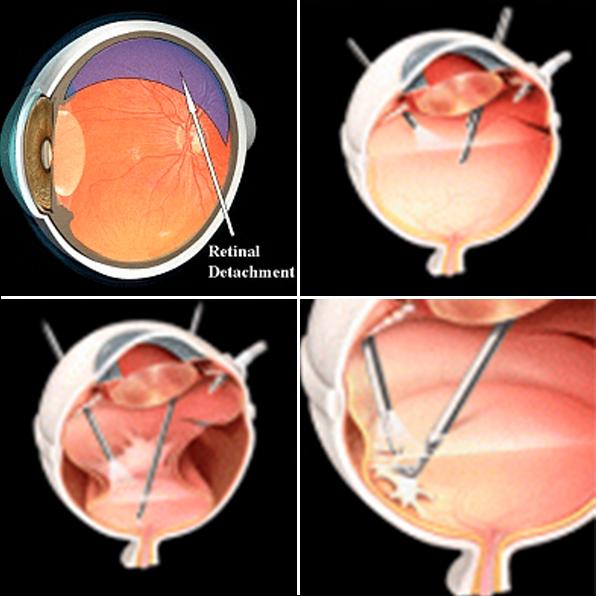
Retinal detachment is a serious ocular condition that occurs when the retina peels away from its underlying supportive tissue. Medical experts emphasize the urgency of treatment to prevent permanent vision loss. The primary risks include sudden flashes of light, floaters, and a curtain-like shadow over the field of vision. If left untreated, the detachment can lead to blindness in the affected eye. Surgeons typically intervene with procedures such as pneumatic retinopexy, scleral buckle, or vitrectomy, aiming to reattach the retina and restore its function.
Recovery can vary depending on the severity of the detachment and the surgical method used. Patients are usually advised to avoid strenuous activities and follow strict positioning instructions, especially after pneumatic retinopexy. Follow-up appointments are critical to monitor healing and detect any postoperative complications. Below is a brief overview of typical recovery milestones:
| Recovery Stage | Timeline | Key Recommendations |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Healing | First 1-2 weeks | Avoid heavy lifting, keep head positioned as directed |
| Vision Improvement | 4-6 weeks | Regular check-ups, report any flashes or floaters immediately |
| Full Recovery | 3-6 months | Gradual return to normal activities, continued monitoring |
- Early diagnosis is essential to maximize the chances of successful vision recovery.
- Post-surgery care often includes medications to prevent infection and inflammation.
- Visual outcomes depend largely on the extent of detachment and how quickly treatment is initiated.
Team Officials Recommend Careful Monitoring and Gradual Return to Play for Davis
Following the successful surgery to repair the detached retina, the medical and coaching staff have emphasized the importance of cautious monitoring throughout Davis’s recovery period. They underscored that rushing back into competitive play could jeopardize both his immediate health and long-term vision stability. Regular assessments, including eye exams and physical evaluations, will be integral to tracking his progress.
To ensure a safe and effective return, the team has outlined a phased rehabilitation plan focusing on gradual reintroduction to training and gameplay:
- Initial rest period with no physical activity for 2-3 weeks
- Light conditioning and non-contact drills beginning in week 4
- Progressive on-court sessions with close medical supervision starting around week 6
- Final clearance contingent on complete recovery and absence of complications
| Recovery Stage | Timeframe | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Rest & Healing | Weeks 1-3 | Minimize eye strain |
| Light Activity | Weeks 4-5 | Non-contact drills |
| On-Court Training | Weeks 6-8 | Gradual increase in intensity |
| Full Return | Week 9+ | Clearance for competitive play |
To Conclude
As Davis begins his recovery following the successful surgery to repair his detached retina, the Dallas Mavericks and their fans will be closely monitoring his progress. The team has yet to announce a timeline for his return to the court, but medical staff remain optimistic about his prognosis. Updates are expected in the coming weeks as Davis undergoes rehabilitation and continues to receive care.